Cybersecurity compliance represents one of the most critical challenges facing UK small and medium-sized enterprises today. With approximately 40% of UK businesses experiencing cyber attacks in the past year, the stakes have never been higher. For SMEs operating with limited resources, understanding and implementing proper cybersecurity compliance isn't just about avoiding fines: it's about protecting your business's future.
This guide provides everything you need to navigate the complex landscape of UK cybersecurity regulations and build a robust compliance framework that protects your business while supporting growth.
Why Cybersecurity Compliance Matters for Your Business
Cybercriminals specifically target SMEs because they assume smaller businesses lack the comprehensive protections of larger corporations. The consequences extend far beyond immediate financial losses. A single data breach can result in direct theft, irreparable damage to your company's reputation, and severe legal liabilities under UK data protection laws.
The regulatory environment has intensified significantly. Over three-quarters of European compliance professionals report their workload increased by more than a third in the past year, with over a third of UK firms facing compliance penalties. This heightened scrutiny reflects both the critical role businesses play in economic stability and the increasingly sophisticated nature of cyber threats.
For many SMEs with constrained budgets and resources, even one serious security incident can threaten the entire business's survival. Proper compliance creates a foundation that protects against these risks while demonstrating professionalism to customers and partners.

Understanding the UK Regulatory Framework
UK GDPR Requirements
Following Brexit, the UK implemented its own version of the General Data Protection Regulation. This applies to all UK businesses that process personal data, regardless of size. If your business handles customer information, employee records, or any identifiable personal data, you must comply with UK GDPR.
The regulation establishes fundamental principles requiring you to process personal data lawfully, fairly, and transparently. Data must be collected for specific purposes, remain adequate and relevant, stay accurate and current, and not be retained longer than necessary.
You must establish a lawful basis for processing personal data, whether through explicit consent, contractual necessity, or legitimate business interests. Individuals possess critical rights including access to their data, rectification of inaccurate information, erasure rights, and data portability.
Cyber Essentials Scheme
The UK government developed Cyber Essentials as a straightforward cybersecurity framework designed specifically for businesses of all sizes. This scheme recognizes that 90% of businesses are small enterprises and that most cyber risks can be avoided through basic protective measures.
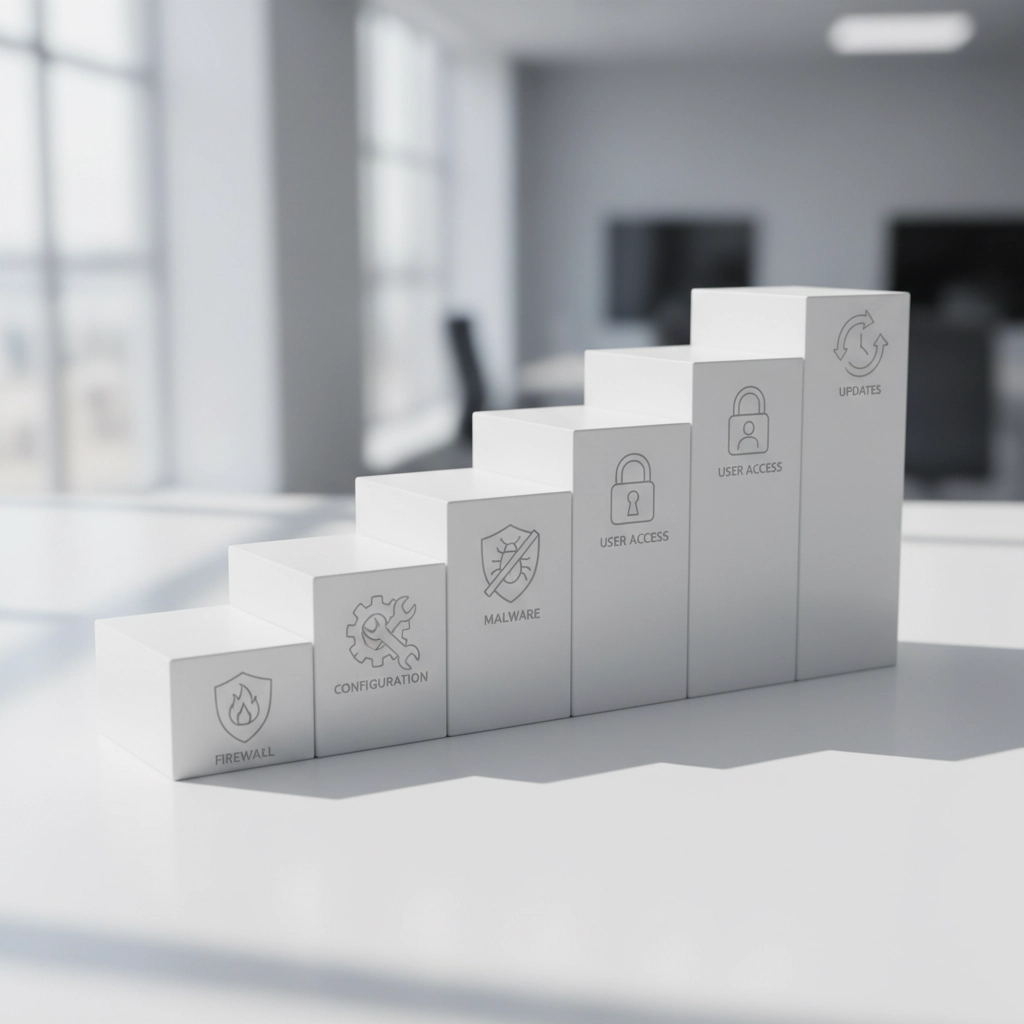
Cyber Essentials covers five critical controls:
- Firewalls: Create secure buffer zones between your business and external networks
- Secure Configuration: Implement the most secure settings for devices and software
- Malware Protection: Deploy properly configured anti-malware software across all systems
- User Access Control: Manage who can access specific services and data
- Patch Management: Keep all devices and applications updated with latest security patches
Certification demonstrates compliance and proves to customers and suppliers that you take cybersecurity seriously. By implementing these controls, businesses can mitigate up to 99% of cyber attacks while ensuring UK GDPR compliance.

Financial Services Regulations
FCA-regulated businesses face some of the UK's strictest cybersecurity requirements. The FCA expects firms to integrate cyber risk considerations into core governance structures, with clear reporting lines and comprehensive security awareness throughout the organization.
Key FCA requirements include documented cyber risk management strategies, regular risk assessments and penetration testing, robust incident response planning, ongoing staff training programs, and direct reporting of major incidents to the FCA.
By March 31, 2025, financial institutions, payment firms, and e-money providers must demonstrate they can withstand, adapt to, and recover from serious operational disruptions.
Core Compliance Requirements for SMEs
Data Protection Obligations
While UK GDPR applies universally, specific considerations exist for smaller organizations. Businesses with fewer than 250 employees receive exemptions from certain record-keeping obligations, unless processing activities create risks to individuals' rights and freedoms.
Data Protection Impact Assessments (DPIAs) are required only for high-risk processing activities, which may not apply to many SMEs' standard operations. Generally, SMEs don't require a dedicated Data Protection Officer unless they process special categories of data on a large scale.
Security Implementation Requirements
Compliance demands continuous effort through regular monitoring and systematic processes. You must implement appropriate technical and organizational measures ensuring security levels match identified risks.
This includes conducting regular security assessments, performing penetration testing where appropriate, and maintaining current documentation of your security posture. The key lies in demonstrating proportionate responses to identified risks rather than implementing every possible security measure.
Incident Response and Reporting
Establish clear incident response procedures enabling your team to react quickly and effectively to security breaches. Under UK GDPR, you must report certain data breaches to the Information Commissioner's Office (ICO) within 72 hours of discovery.
You may also need to inform affected individuals if breaches pose high risks to their rights and freedoms. This requires maintaining accurate contact information and communication templates for rapid response.

Step-by-Step Implementation Guide
Step 1: Conduct Risk Assessment
Begin by identifying all personal data your business processes, where it's stored, who has access, and what threats you face. Document data flows from collection through disposal, noting security vulnerabilities at each stage.
Create a comprehensive inventory including customer records, employee information, supplier data, and any third-party processing arrangements. This inventory forms the foundation for all subsequent compliance activities.
Step 2: Implement Technical Controls
Start with the five Cyber Essentials controls as your security foundation. Configure firewalls to control traffic between your network and the internet, removing unnecessary access points and implementing strong access policies.
Establish secure configurations for all devices and software, removing unnecessary functionality and changing default passwords. Deploy comprehensive malware protection across all systems, maintaining current threat definitions and regular scanning schedules.
Step 3: Establish Access Controls
Implement user access controls based on the principle of least privilege. Employees should access only data necessary for their specific roles. Create clear procedures for granting, modifying, and removing access permissions as job responsibilities change.
Use strong authentication methods including complex passwords, multi-factor authentication where possible, and regular password updates. Monitor access logs to identify unusual patterns that might indicate security breaches.
Step 4: Create Documentation and Policies
Develop comprehensive policies covering acceptable use, data handling, incident response, and business continuity. These policies should be clearly written, regularly reviewed, and accessible to all employees.
Maintain detailed records of data processing activities, security measures implemented, and compliance efforts undertaken. This documentation proves compliance during audits and helps identify areas for improvement.
Step 5: Train Your Team
Implement ongoing staff training programs covering cybersecurity awareness, data protection responsibilities, and incident response procedures. Employees need to understand their role in protecting company data and recognize common threats like phishing attempts.
Conduct regular training sessions complemented by practical testing through simulated attacks or security awareness assessments. Document training completion and update programs based on emerging threats.
Common Compliance Pitfalls to Avoid
Many SMEs fall into predictable compliance traps that can be easily avoided with proper planning. Treating compliance as a one-time project rather than an ongoing process represents the most common mistake. Cybersecurity threats evolve constantly, requiring regular updates to your protective measures.
Neglecting employee training creates significant vulnerabilities since human error accounts for the majority of successful cyber attacks. Even the most sophisticated technical controls fail if employees unknowingly compromise security through poor practices.
Inadequate documentation hampers your ability to demonstrate compliance during audits or investigations. Maintain comprehensive records of all security measures, training activities, and incident responses.
Failing to test security measures regularly means you won't discover vulnerabilities until criminals exploit them. Conduct periodic assessments of all security controls and address identified weaknesses promptly.
Building Long-Term Resilience
Cybersecurity compliance isn't a destination but an ongoing journey requiring continuous attention and improvement. View compliance as an opportunity to strengthen your business rather than merely a regulatory burden.
Establish regular review cycles for all security measures and policies. Technology changes rapidly, and your security posture must evolve accordingly. Schedule quarterly assessments of your compliance status and annual comprehensive reviews of your entire cybersecurity program.
Build relationships with cybersecurity professionals who can provide guidance as your business grows and faces new challenges. Consider working with IT consulting specialists who understand the unique needs of SMEs and can provide cost-effective solutions.
Stay informed about emerging threats and regulatory changes through industry publications, professional associations, and government resources. The cybersecurity landscape evolves continuously, and staying current protects your business and ensures ongoing compliance.

Taking Action Today
Start your compliance journey immediately with these practical first steps. Conduct a basic inventory of all personal data your business processes and assess your current security measures against the Cyber Essentials framework.
Identify the most critical vulnerabilities in your current setup and prioritize addressing these risks. Focus on implementing basic protective measures before advancing to more sophisticated security controls.
Document everything you do, from risk assessments through security implementations. This documentation proves your compliance efforts and guides future improvements.
Remember that cybersecurity compliance protects not just your business but also your customers, employees, and partners who trust you with their information. By taking systematic action today, you build a foundation that supports sustainable business growth while meeting all regulatory requirements.
The investment in proper cybersecurity compliance pays dividends through reduced risk, increased customer trust, and protection of your business's future. Start with the basics, build systematically, and maintain your commitment to continuous improvement.
