Manufacturing operations face an unprecedented level of risk from cyberattacks, natural disasters, and system failures. A single hour of downtime can cost manufacturers anywhere from £50,000 to £500,000, depending on the scale of operations. Yet many manufacturing companies still operate without comprehensive disaster recovery plans, leaving their production lines, supply chains, and revenue streams vulnerable to catastrophic disruption.
Building robust IT infrastructure for unpredictable manufacturing environments requires strategic planning that addresses both information technology and operational technology systems. This guide provides actionable steps to develop disaster recovery capabilities that protect your manufacturing operations and ensure business continuity.
Understanding Manufacturing-Specific Disaster Recovery Risks
Manufacturing environments present unique challenges that standard IT disaster recovery approaches often fail to address. Production systems integrate complex networks of programmable logic controllers, human-machine interfaces, and supervisory control systems that require specialized protection strategies.
Identify your critical manufacturing systems by categorizing them into three priority levels. Priority one includes systems that directly control production processes, safety systems, and quality control mechanisms. Priority two encompasses inventory management, maintenance scheduling, and supply chain coordination tools. Priority three covers administrative functions and reporting systems.
Document the interdependencies between your IT and operational technology systems. Map how ERP systems connect to manufacturing execution systems, how quality management databases link to production line controls, and how supply chain management platforms integrate with inventory tracking systems. This mapping reveals potential failure points and helps prioritize protection efforts.
Calculate your maximum tolerable downtime for each system category. Production lines typically require recovery within 15-30 minutes to prevent significant financial impact. Administrative systems may tolerate several hours of downtime without major consequences. Use these calculations to establish Recovery Time Objectives (RTO) and Recovery Point Objectives (RPO) for each system category.
Building Disaster Recovery Infrastructure
Implement high-availability clusters for mission-critical manufacturing systems. Configure automatic failover mechanisms that transfer workloads to backup systems within minutes when primary systems fail. Deploy clustered database servers, redundant network switches, and backup power systems to eliminate single points of failure.
Deploy cloud-based ERP solutions that provide both scalability and remote operability. Cloud platforms enable you to maintain production scheduling, inventory management, and supplier coordination even when physical facilities become inaccessible. Configure multi-region deployments to protect against regional disasters and ensure continuous access to critical business functions.
Establish network segmentation between IT and OT systems using industrial firewalls and secure gateways. Create isolated recovery environments that can operate independently if either network becomes compromised. Implement defense-in-depth strategies that protect production systems from both external cyberattacks and internal IT system failures.

Configure real-time data replication for critical manufacturing databases. Implement continuous data protection that captures changes as they occur and maintains synchronized copies in geographically separated locations. Use application-consistent snapshots that preserve data integrity across interconnected manufacturing systems.
Deploy backup power infrastructure that supports both IT systems and essential production equipment. Install uninterruptible power supplies for immediate protection and backup generators for extended outages. Test power failover procedures regularly to ensure seamless transitions during actual emergencies.
Disaster Recovery Implementation Framework
Develop recovery procedures that address both technology restoration and operational continuity. Create detailed runbooks that specify step-by-step recovery processes for different disaster scenarios. Include procedures for restoring production line configurations, quality control parameters, and safety system settings.
Establish clear communication protocols for disaster scenarios. Define notification procedures for key personnel, suppliers, and customers. Create communication templates that provide status updates and expected recovery timelines. Implement backup communication systems that function when primary networks fail.
Train manufacturing teams on disaster recovery procedures specific to their operational areas. Conduct regular drills that simulate different failure scenarios and measure response effectiveness. Cross-train personnel to ensure critical functions can continue even when key team members become unavailable.
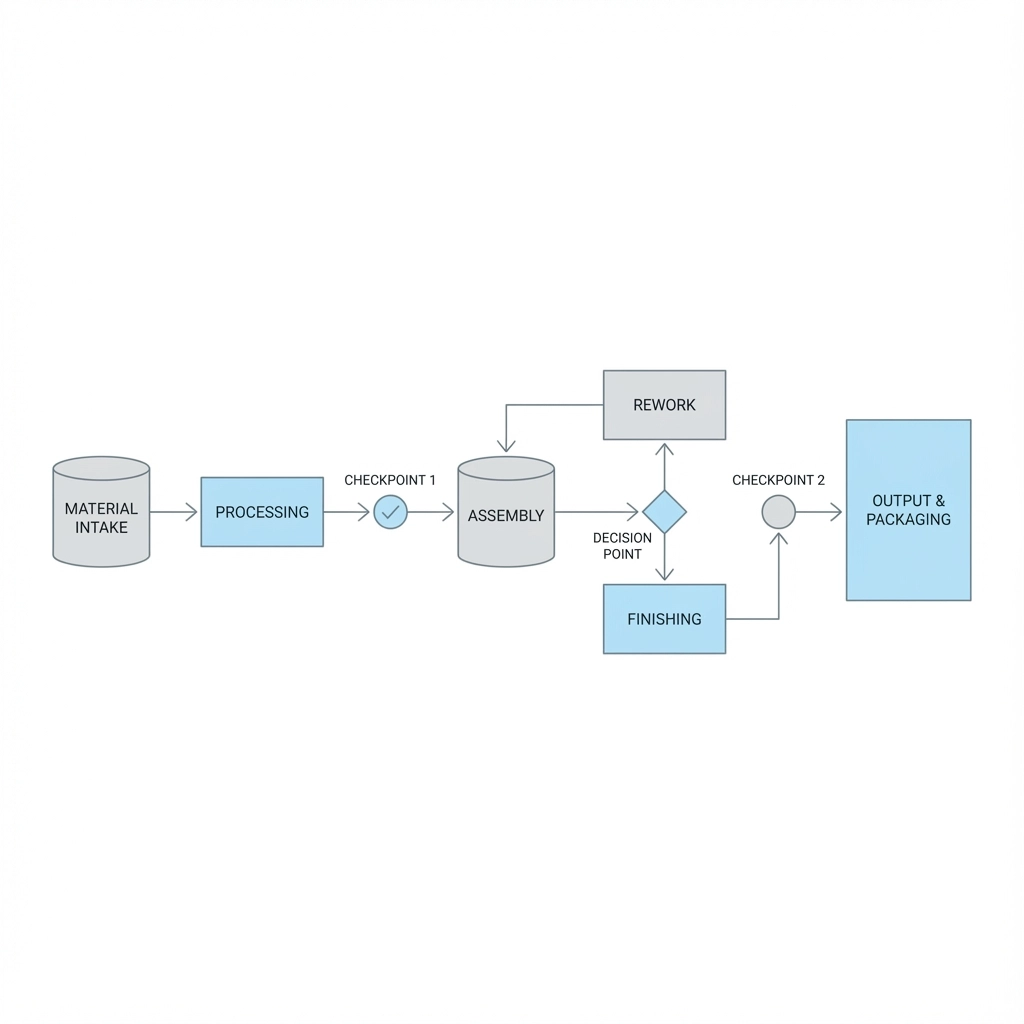
Implement automated testing procedures that validate disaster recovery capabilities without disrupting production operations. Use virtualized environments to test recovery processes and verify data integrity. Schedule monthly tests of backup systems and quarterly tests of full recovery procedures.
Create vendor management protocols that ensure rapid replacement of critical hardware and software components. Establish service level agreements with key suppliers that guarantee priority support during emergencies. Maintain strategic inventory of critical spare parts and backup equipment.
Testing and Continuous Improvement
Execute tabletop exercises that simulate realistic disaster scenarios specific to manufacturing environments. Test scenarios including ransomware attacks on production systems, natural disasters affecting facility access, and critical supplier disruptions. Evaluate response effectiveness and identify improvement opportunities.
Perform regular recovery testing using non-production environments that mirror your manufacturing systems. Validate that restored systems maintain proper configurations for production equipment, quality standards, and safety protocols. Document test results and track improvement metrics over time.
Monitor recovery infrastructure continuously using automated health checks and performance monitoring. Implement alerting systems that notify administrators when backup systems experience issues or when replication processes fall behind schedule. Address infrastructure problems before they impact recovery capabilities.

Update disaster recovery plans quarterly to reflect changes in manufacturing processes, technology deployments, and business requirements. Review and adjust RTO and RPO targets based on operational changes and cost considerations. Incorporate lessons learned from actual incidents and testing exercises.
Establish metrics that measure disaster recovery effectiveness and business impact. Track mean time to recovery for different system categories. Monitor data loss incidents and their impact on production quality. Use these metrics to justify investments in improved disaster recovery capabilities.
Integration with Digital Transformation Strategy
Align disaster recovery planning with broader digital transformation initiatives. Implement cloud-first strategies that inherently provide better disaster recovery capabilities than traditional on-premises deployments. Use digital transformation projects as opportunities to eliminate legacy systems that create disaster recovery vulnerabilities.
Leverage IoT sensors and predictive analytics to identify potential system failures before they cause production disruptions. Implement condition-based monitoring for critical manufacturing equipment and IT infrastructure. Use machine learning algorithms to predict failure patterns and schedule preventive maintenance.
Deploy software-defined infrastructure that enables rapid provisioning of recovery resources. Use containerized applications that can be quickly deployed across different environments. Implement infrastructure-as-code practices that enable consistent recovery environment configuration.
Creating a Culture of Preparedness
Establish disaster recovery as a core business competency rather than an IT-only responsibility. Include disaster recovery considerations in all manufacturing process changes and technology deployments. Create cross-functional teams that include operations, engineering, and IT personnel.
Develop key performance indicators that measure disaster recovery readiness across manufacturing operations. Track metrics including backup success rates, test completion rates, and training participation levels. Use these metrics to drive continuous improvement and maintain organizational focus.
Regular disaster recovery planning protects manufacturing operations from unpredictable disruptions while supporting broader digital transformation objectives. Implement these strategies systematically to build resilient manufacturing capabilities that maintain operations regardless of external challenges.
For comprehensive disaster recovery planning tailored to your manufacturing environment, contact our virtual IT directors who specialize in manufacturing IT strategy and operational continuity planning.
